This article is the first in a series on Injection Mould Lifecycle Management, and targets the Planning phase.
It takes less time to do a thing right, than it does to explain why you did it wrong . . .
– Henry Wadsworth
. . . and tons of more time to redo it correctly.
The same holds true when procuring a new asset.
Ask anyone in the manufacturing industry – injection moulds are exorbitant, to say the least. To get them wrong the first time casts a dark shadow of costly re-investment. Edwards Deming sums it up aptly: A bad system will defeat a good person every time. Preventing such unfavourable outcomes necessitates a proper system and process flow to achieve the desired objective, which can be a mould for a brand-new component design (Innovation) or a mould for an already existing design (Repeat).
Five Stages of Mould Lifecycle Management
There are five phases in the overall mould lifecycle management:

This article is the first in a series on Injection Mould Lifecycle Management, and targets the Planning phase.
Planning Stage
Planning is the most important determinant of success for any project. Successful commissioning of a mould is the result of insightful efforts of various teams working in close coordination. Therefore, it is of utmost importance that each member is aware of the objective behind the commissioning of the mould.
The Planning phase must answer questions such as:
- What are we going to do?
- How are we going to do it?
- What are each team member’s deliverables?
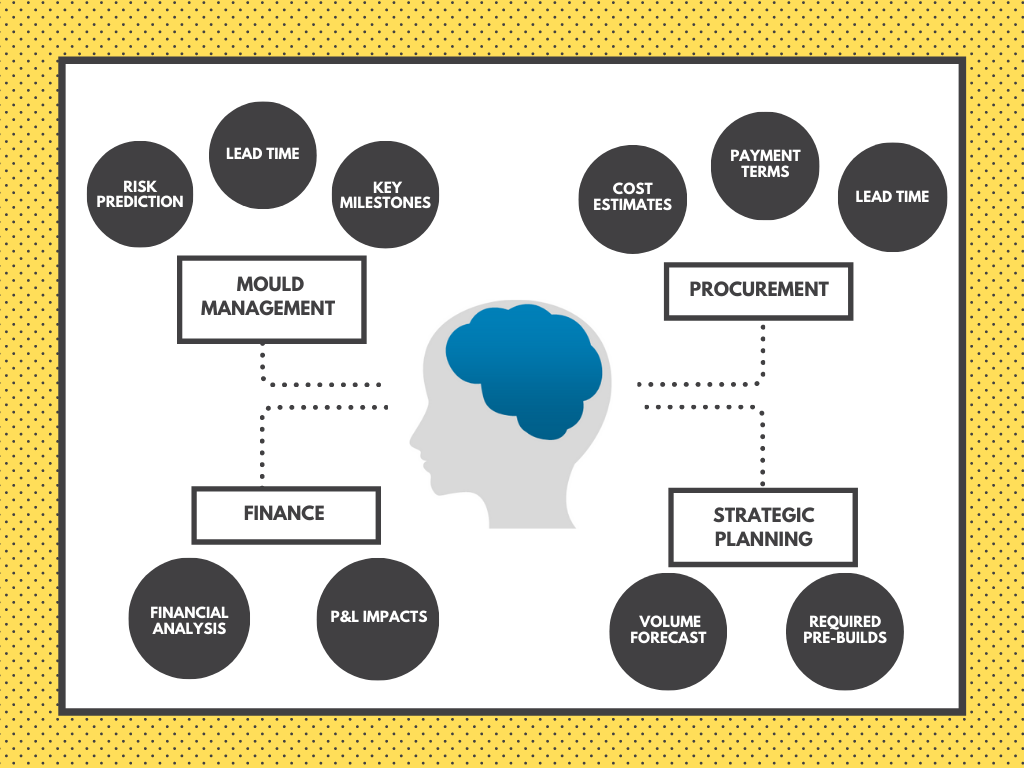
For the company top brass, a mould represents a project which involves investment to deliver value. In order to get it approved, you must build a proper Business Case and present it to the Key Decision Makers (KDM).
Components of the business case are:
- Executive Summary: Is the gist of your business case and should highlight the most important factors for the KDM to scan through. These include:
○ Overall Costs
○ Payback Time
○ Overall Lead Time
This way, they will understand the reason for request of capital and the value returned to the organization.
After all, capital is the starting point of implementation of any idea!
- Project Description: Specific information explaining:
○ Where the opportunity is observed;
○ What is the objective of building a new mould or refurbishing an existing one; and
○ What will be the outcome of the new mould build/mould refurbishment?
- Assumptions: List down all the open assumptions. And ensure everyone on the team is aware of the same. This avoids any delay in mould build or any issues with mould life.
- Volume Forecast: Of the various methods available for volume forecast, consider the YoY increment technique on a priority basis. This helps the team understand the:
○ Required number of cavities on an individual mould; and
○ Total number of moulds required to meet the current or forecasted demand.
- Cost Estimates: Additional costs are always required above the cost of new mould build or mould refurbishment. Incorporate these costs in the business case to avoid subsequent unavailability of capital, something that will jeopardize project completion.
- Alternate Options: List out all the alternatives which were considered before landing on the current project proposal. This could include a comparison of:
○ Various mould makers for manufacturing or refurbishing the mould; or
○ Different cavities required on the moulds.
- Financial Analysis: Represents the conversion of strategy into measurable financial outcome. This is the most important part of business case and helps the team take a call on whether it is viable to invest funds in the mould project.
Such analysis considers all the costs which will be incurred in order to calculate a Profit & Loss Statement and showcase the value obtained against the investment. - Risk: Are the major speed breakers as some of them cannot be predicted at all. List the risks associated with cost, schedule, strategy, operations, and the like. Thereafter, conduct a brainstorming session to map out a mitigation plan if the risks materialize during the later stages of mould manufacturing or refurbishment.
- Team Members: Members from various teams will manage the entire mould life cycle. With this in mind, introduce all the teams to each other with clear explanations of their roles and responsibilities. This helps them connect with the relevant members when in need.
- Key Milestones: Map all the key milestones along with a timeline. Plan and track the defined timeline for successful commissioning of a new mould or refurbishment of an existing one.
- Equipment Listing: Note down the required equipment such as Jigs & Fixtures, IMM, and availability of labour.
- Site Qualification: Is necessary in case the mould will be shipped to a location other than the one where it is manufactured.
- Inventory Forecasting: Have the estimated inventory levels in place at predetermined future dates to prevent last minute hold ups.
Moving Ahead
Only when these factors are taken care of and the KDMs approve the business case, the mould life cycle moves on to the next phase. Flawless planning is the first step in the right direction. Get it right and . . . well – a well begin is half done!
Efficient Innovations has successfully delivered foolproof Mould Lifecycle Management solutions for over 10 years to esteemed clients across the globe. It goes without saying that all these starts with visionary planning. Write to us at www.efficientinnovations.in to know more.





