Why Track Mould Condition?
In our previous articles of Preventive Mainenance (Part 3.1) and Corrective Maintenance (Part 3.2), we understood the importance of mould maintenance and its impact on mould life. This article continues the same idea but with a different viewpoint on how to track the maintenance and health of the mould.
As a business owner, you always want to maximise returns with minimal investments. Similarly, a business needs to ensure the optimal condition of assets, again with minimum investment. How do you achieve all this? By tracking your moulds for every maintenance cycle as well as any investment made to improve the mould health.
Requisites of the Tracking Process
Tracking mould maintenance is easier if you have a limited number of moulds. But what if you are a company with hundreds of moulds? Or are a colossal MNC with thousands of moulds at multiple locations spread far and wide across the Globe. In such a case, it is of utmost importance to institute a process which helps you track the maintenance of every asset.

Your process must help you achieve the below objectives:
1.Data Repository: As a company, you should have complete knowhow of all the assets which you own or are running at your facility. It is said that with great data comes greater issues. Hence, data hygiene and transparency are of crucial importance. The data repository will be super helpful to keep track of all your assets and capture important data in one place which can be accessed later or shared with the required members.
2.Preventive Maintenance (PM) Log: Every individual mould will have its own preventive maintenance cycle and so it is of utmost important to have the maintenance schedule in place. This document should include every detail of PM such as whether the PM was performed at the scheduled date, which actions were performed, what was the duration of the down time, and who performed it.
3.Issue Log: Issues will always arise in your mould, no matter what you do. Hence, it is advantageous to document all the issues that were observed on the mould during its production run period as well as what was the action plan performed to mitigate the same. This can also act as a database to handle similar issues in the future.

~ Repair Tracker: It is not recommended to refurbish the mould more than 3 times. Maintaining a record of all the refurbishments conducted on the mould and when they were performed along with the scope and cost of the same helps in correctly determining when the mould is not in the required condition and when refurbishing is out of question.
~ Mould Health: Last and perhaps the most important is the dynamic data of moulds such as age, total shots it has run, status of the production run, and current condition on the mould. Such data helps decide the necessary actions.
Once the process is in place, the next step is to make sure that it is performed on a scheduled cycle. The scheduled cycle could be daily, weekly, monthly, or quarterly based on the number of moulds and the availability of resources to conduct the same since it is a time-consuming activity.
The process will also help you set up strategies to maintain your mould and ensure the moulds are in the most optimised condition. All in all, this will improve their life expectancy.
Strategy
Mould condition is the primary factor to consider when designing the strategy. Secondary considerations include category, sub-category, or regions.
Below are few points which should be considered while devising a strategy plan for your mould:
Poor Moulds can be a result of multiple issues, which need immediate attention. Careful consideration on the volume forecasts, life of the mould, and previous history of the mould would help the assessor devise an action plan for rework, replacement, or refurbishment.
The mould is inspected for the required scope, after which a final quote with lead time, cost, and scope of work is shared with the stakeholders.
If it is a primary mould or the only mould supporting the business, make sure that enough inventory levels are maintained before the mould is down for the required action plan.
Fair Moulds are those in whom minor issues are observed. With addition to the considerations for Poor moulds, Fair moulds require additional perspective on the warranty, health, and supplier’s confident to run the mould in its current condition.
For fair moulds, we do not need immediate attention. What we need is to monitor the health more carefully so that the mould undergoes the required mitigation action when needed.
Good Moulds are those on which no issues are observed. For these moulds, it is important to ensure the preventive maintenance is done as per the schedule. A good mould is also checked for its utilization based on the capacity and volume. This gives indication if additional mould is required for that structure.
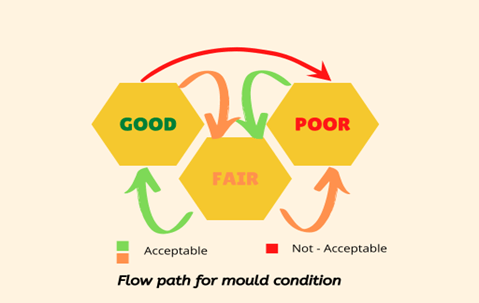
However, there will sometimes be totally unexpected events when the mould suddenly breaks down. The breakdown is not forecasted and makes the mould go from Good to Poor. This is a cause of concern but is something no one can do anything about. But if the mould condition changes from Good to Poor without such a black swan event, then there is some gap in your process and optimization of the same is needed.
“Efficient Innovations has been supporting its clients to track thousands of moulds spread across multiple continents. That apart, we create strategies to improve the mould condition. Get in touch with us for a seamless mould tracking and maintenance experience”





